The terms VPS and RDP are often confused, but choosing the wrong tool for the job can be a critical mistake. The difference is simpler than you think: comparing a VPS to RDP is like comparing a car to its key.
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is the vehicle, a powerful, private environment for your projects. The Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is the key, the tool you use to access and control that vehicle. They serve different purposes but often work together. This guide will explain the key differences to help you choose the right solution for your needs.
What is a VPS (Virtual Private Server)?

A Virtual Private Server, or VPS, is a powerful and flexible hosting solution. To understand what a VPS is, let’s use a simple analogy. Imagine a massive, powerful physical computer, a Dedicated Server. Renting that entire server for yourself can be expensive. Virtualization technology allows that single physical server to be partitioned into multiple, independent virtual servers.
Think of the dedicated server as a large apartment building. A VPS is like renting your own private apartment within that building. You have your own guaranteed space, your own front door (security), and you can decorate it however you like (install your own software). You have your own kitchen and bathroom (dedicated resources), and your neighbor’s activities don’t directly impact your living space.
So, what is a VPS used for? Its uses are incredibly diverse. Businesses host websites and applications on them, developers use them as sandboxed testing environments, and traders run automated software on them 24/7. It’s essentially a private, remote computer that you have complete control over.
How a VPS Works?
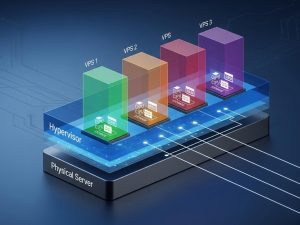
The magic behind a VPS is a piece of software called a Hypervisor. The hypervisor sits on top of the physical server’s hardware and Operating System. Its job is to create and manage the virtual machines (the VPSs). It carves up the physical server’s resources—CPU cores, RAM, and disk space, and allocates a dedicated portion of each to every VPS. This ensures that even though you’re sharing the physical hardware, the performance of your VPS isn’t affected by other users on the same server. Each VPS operates as a completely separate machine.
Key Characteristics of a VPS
- Dedicated Resources: When you purchase a VPS plan, you are guaranteed a specific amount of RAM, CPU, and storage. These resources are yours alone and are not shared with other users.
- Root Access: You get full administrative or “root” access to your server. This means you have complete control to install any compatible Operating System (like various versions of Linux or Windows), install custom software, and configure the server environment precisely to your needs.
- Isolation: Your VPS is completely isolated from other virtual servers on the same physical machine. A security breach or a crash on another user’s VPS will have no effect on yours, providing a secure and stable environment.
What is RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)?

Now, let’s shift gears to RDP. The Remote Desktop Protocol, or RDP, is not a server or a computer. As its name suggests, it’s a protocol, a set of rules and instructions that allows one computer to connect to and control another computer over a network. So, what is RDP? It’s the language that enables Remote Access.
Developed by Microsoft, RDP is built into most versions of the Windows operating system. It was designed to give users and administrators a full graphical interface to interact with a remote machine, making it feel as if they were sitting right in front of it.
If a VPS is the apartment, RDP is the secure communication system that lets you talk to the doorman and see what’s happening inside your apartment from miles away. It’s a method of connection, not the destination itself.
How RDP Works?
The process is based on a client-server model. The computer you want to control (the “remote” machine) runs the RDP server software. The computer you are using to connect (the “local” machine) runs the RDP client software. When you initiate a connection, RDP captures the graphical interface of the remote machine, compresses it, and sends it over the network to your client. It also sends your keyboard strokes and mouse movements back to the remote machine, allowing you to interact with it in real-time. How does RDP work? In short, it streams a desktop experience to you.
Key Characteristics of RDP
- Graphical Interface Access: RDP’s main feature is providing a user-friendly graphical desktop experience, unlike command-line interfaces like SSH.
- Remote Control: It offers comprehensive control over the remote machine, allowing you to run applications, access files, and manage system settings.
- Platform Dependency: While there are RDP clients for many operating systems (macOS, Linux, iOS, Android), the server component that allows incoming connections is a native feature of Windows.
The Main Differences Between VPS and RDP (Comparison Table)
To truly understand the difference between VPS and RDP, a direct comparison is the best approach. The fundamental difference is that a Virtual Private Server is a type of hosting environment, while the Remote Desktop Protocol is a communication tool for remote access. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Feature | VPS (Virtual Private Server) | RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) |
| Nature | An Environment: A virtualized server that acts as a standalone computer. | A Protocol: A set of rules for communication to enable remote control. |
| Purpose | Hosting: Used for hosting websites, applications, databases, and running software 24/7. | Access: Used to remotely access and control another computer’s desktop. |
| Resources | Dedicated: You get a guaranteed, isolated pool of CPU, RAM, and storage. | Shared (Typically): When you buy an “RDP account”, you’re sharing a machine’s resources with many other users. The protocol itself uses network bandwidth. |
| Control/Access | Root/Admin Access: Full control to install OS, software, and configure the entire environment. | User-level Access: You typically get a standard user account with limited permissions. You can’t install most software or change system settings. |
| Operating System | Flexible: You can choose to install various Linux distributions or Windows Server. | Primarily Windows: RDP is a native Microsoft technology for connecting to Windows-based machines. |
| Cost | Subscription-based: You pay a monthly or annual fee for the server resources. | Included with Windows: The protocol is free. However, “RDP Accounts” or “RDP Servers” are sold as low-cost services with shared resources. |
| Security | Isolated Environment: Your server is sandboxed from others, offering strong security. You are responsible for securing your OS. | Dependent on Host: Security relies entirely on the configuration of the host machine. RDP ports can be a target for cyberattacks if not properly secured. |
Common Use Cases: When to Choose VPS vs. When to Use RDP
Knowing the technical differences is one thing; knowing when to use each is what really matters. So, when is RDP better than VPS, and vice versa? Let’s look at practical scenarios.
Choose a VPS If…
- You Need to Host a Website or Application: This is a primary use case. A VPS provides the stable, always-on environment and necessary server software (like Apache or NGINX) to run a website. You cannot host a website on a simple RDP account.
- You Are Running Automated Software 24/7: This is especially relevant for Forex Trading. A VPS for trading allows you to run platforms like MetaTrader with Expert Advisors (EAs) continuously, without interruption and with low latency to broker servers, even when your local computer is off.
- You Require Full Control and Customization: If you need to install a specific version of PHP, run a unique database, or set up a custom software stack for development, you need the root access that only a VPS can provide.
- You Need Guaranteed Performance: For applications that require consistent resources, like a busy e-commerce site or a small game server, the dedicated resources of a VPS are essential. The topic of VPS vs RDP for gaming is clear: you host the game server on a VPS; you might use RDP to manage the server, but not to play the game.
Choose RDP If…
- You Need to Access Your Office Computer from Home: This is the classic Remote Work scenario. RDP allows you to connect to your work machine and access all your files and applications exactly as you left them. Your company’s IT department manages the server; you just use RDP as the key.
- You Are Providing or Receiving Technical Support: Tech support teams use RDP (or similar tools) to remotely view and control a user’s computer to troubleshoot problems directly.
- You Need to Manage a Windows Server: If you have a dedicated server or a Windows VPS, RDP is the standard tool you’ll use to log in and manage it graphically.
- You Purchased a Simple “RDP Account”: Sometimes people buy cheap RDP accounts simply to have a remote desktop in a different geographic location for tasks like browsing or managing social media accounts. These accounts have very limited permissions.
Can You Use RDP with a VPS? Understanding the Relationship

This is where the confusion peaks, and also where everything clicks into place. Can you use RDP with a VPS? The answer is a resounding yes. In fact, it’s the standard way to interact with a server running a Windows Operating System.
When you buy vps , you’re renting a remote computer that has no physical screen or keyboard. RDP is the technology that acts as your virtual screen and keyboard, giving you full graphical control over your Windows VPS. After you connect using the IP and login details from a provider like Mixal, your server’s desktop appears right on your local machine.
To make this relationship clear, let’s break down the most important points:
- RDP on VPS is Standard Practice: This phrase simply means using the RDP tool to log into and manage your Windows VPS. They work as a team; one is the server, the other is the key to access it.
- A Windows VPS is Not an RDP Account: This is a critical distinction. A VPS gives you a private, dedicated server with full admin rights. An “RDP account” is just a cheap, shared user login on someone else’s server with heavy restrictions and no administrative power.
- RDP Itself is Free: You don’t pay extra for using RDP. The protocol is a built-in part of the Windows OS on your VPS. Your monthly fee is for the server’s hardware resources (CPU, RAM, etc.), not the access method.
- Linux Uses SSH: For Linux servers, the equivalent tool is not RDP. Instead, you’ll use SSH (Secure Shell), which provides secure, command-line access to manage your server.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each
To provide a comprehensive overview in the VPS vs RDP comparison, it is crucial to assess the specific pros and cons of each option.
VPS: Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any technology, a Virtual Private Server has its own set of strengths and weaknesses depending on your needs. Let’s take a balanced look at both the advantages and disadvantages of using a VPS, starting with its strengths.
VPS advantages:
- Full Control: Root access allows for complete customization of the server environment.
- High Performance: Dedicated and guaranteed resources mean your applications run smoothly and consistently.
- Enhanced Security: The isolated nature of a VPS means you are protected from other users on the host node. You control your own security settings. This directly answers: Is VPS more secure than RDP? The VPS environment is far more secure than a shared RDP account.
- Scalability: It’s easy to upgrade your CPU, RAM, and storage as your needs grow.
VPS Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: A VPS is more expensive than a shared hosting plan or a simple RDP account due to the dedicated resources.
- Management Responsibility: With great power comes great responsibility. You are in charge of managing, securing, and updating your server, which requires some technical knowledge.
RDP: Advantages and Disadvantages
As a powerful tool for remote access, RDP has clear benefits but also some important drawbacks. Let’s weigh them up, starting with what it does well.
RDP Advantages:
- Ease of Use: Connecting via RDP is straightforward and provides a familiar graphical desktop.
- Convenience: It allows you to access a remote computer from anywhere in the world as if you were right there.
- Cost-Effective: The protocol is built into Windows. RDP accounts, while limited, are very cheap.
RDP disadvantages:
- Security Risks: The RDP port is a frequent target for brute-force attacks. Security is entirely dependent on the host machine’s configuration, including strong passwords and firewalls.
- Limited Functionality (on RDP accounts): Standard RDP accounts do not give you administrative rights, severely limiting what you can do.
- Performance Issues: RDP performance is sensitive to network latency. On shared RDP servers, performance can be poor if other users are consuming too many resources.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
So, VPS vs RDP which is better? The answer is clear: they are not competing options for the same job. The right choice depends entirely on your goal.
- If your goal is to host something, a website, a web application, a database, or a 24/7 trading bot, you need a VPS. It provides the power, control, and dedicated resources necessary for the job.
- If your goal is simply to access another computer remotely, like your office PC, a family member’s computer for tech support, or the Windows VPS you just bought, you need RDP. It is a tool for remote access.
For many users, particularly in the trading and business communities, the solution isn’t one or the other; it’s both. They Buy vps running Windows Server to host their critical applications and then use RDP as their daily tool to log in, manage, and interact with that server.
By understanding that a VPS is the destination and RDP is the pathway, you can move forward and select the exact technical solution your project requires.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Is RDP a type of VPS?
No, this is a common misconception. RDP is a protocol that is a set of rules for communication. A VPS is a virtual server, which is a computing environment. You use the RDP protocol to connect to and control a Windows-based VPS.
- Can I host a website on an RDP account?
No. A standard RDP account gives you a user profile on a shared computer with no administrative privileges. You cannot install the necessary server software (like Apache or IIS) or configure DNS settings. To host a website, you need a hosting solution, such as a VPS.
- What is the difference in cost between a VPS and an RDP server?
A VPS is more expensive because you’re paying for guaranteed, private resources (CPU, RAM) and full administrative control. In contrast, an RDP account is much cheaper because you’re simply sharing a single server’s resources with many other users.
- Which is better for running a 24/7 bot or software?
A VPS is the only suitable choice. Software that needs to run 24/7, like a trading bot or a monitoring script, requires a persistent and stable environment that you control completely. A VPS ensures your software stays online and active, independent of your personal computer.
- Do you need technical skills to use a VPS? What about an RDP?
Using RDP is as easy as using Windows and requires no special skills. In contrast, managing a VPS demands basic server administration knowledge for handling updates and security. For an easier alternative, you can opt for a “managed VPS” plan, where the provider handles all technical tasks.