What is a Virtual Private Server (VPS)? In this article, we will define servers, explain the concept of VPS to develop a deeper understanding, and explore how VPS works, including how to manage it and its control panels. Then, we’ll discuss the applications and features of VPS. Additionally, we’ll cover the types of VPS based on geographical location, such as Canada VPS or Germany VPS, each of which can come with different operating systems, known as Linux VPS and Windows VPS today. Finally, we’ll address all your questions regarding Virtual Private Servers.
Initial Definition of a Server
To understand what VPS is, we first need to learn about servers. Simply put, a server can be thought of as a powerful computer that has some essential features:
- It’s always on.
- It always has access to high-speed internet.
- It is equipped with powerful hardware.

Based on this definition, if you were to configure a computer so that it met these conditions, technically it could act as a server. However, because of the significant costs involved in acquiring and maintaining such a system, this idea for most people stays just that—an idea.
In practice, whether for individuals or companies, the solution is to use ready-built servers provided by hosting service companies.
If you’re wondering what a VPS is and what it’s used for, you should know that servers are employed for many purposes: hosting websites and web applications, running game servers, and more. In today’s world, servers play a fundamental and irreplaceable role in our daily lives.
History of Virtual Servers
The history of virtual servers dates back to the development of virtualization technology introduced by IBM in the 1970s. At that time, IBM unveiled an innovative technology that allowed multiple users to share the resources of a large and powerful computer, such as mainframes.
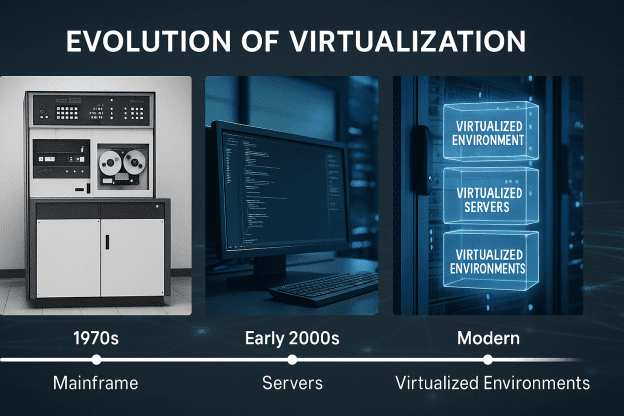
This innovation—the initial concept of virtualization—helped organizations optimize the utilization of their costly hardware resources.
Advances in Computing and Internet Technologies
In subsequent decades, the rapid advancement in processing power and Moore’s Law (which predicts that processor power roughly doubles every 18 months) drastically improved computing capacity and capabilities. However, the core issue remained: most servers, due to their specialized applications, were utilizing only a small fraction of their processing capacity.
For example, if a physical server was utilizing only 15% of its capacity, the remaining resources were essentially going to waste.
Significant Changes in the Early 2000s
With the explosive growth of the internet in the early 2000s, there was a growing need for more efficient solutions for managing hardware resources. During this period, virtualization technology matured enough to facilitate more efficient resource utilization. The emergence of hypervisors marked a major turning point.
Hypervisors are software tools that allow multiple virtual machines or virtual servers to run on a single physical server. By sharing hardware and software among different machines, they increased efficiency and improved resource utilization by up to 60%.
How it Differed from Previous Methods
Prior to the advent of hypervisors, servers were dedicated to running one specific application or service. This approach increased costs and complicated hardware management. Virtualization allowed organizations to deploy multiple virtual servers with high reliability on a single physical server. This transformation reduced costs, improved flexibility, and increased efficiency.
The Key Role of Virtual Servers in Today’s World
Today, virtual servers are a vital part of information technology infrastructure. This technology enables businesses to offer scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient services. Additionally, virtual servers serve as the backbone of cloud computing, providing better resource management, support for high user volume, and adaptability to changes.
Understanding Virtualization Technology
As you may know, hardware systems are managed through their operating systems. This means that once you’ve procured a system and installed an operating system like Windows on it, you can start utilizing it. Now, if for some reason you wish to install and use another operating system on the same system, you will need virtualization technology to make this possible.
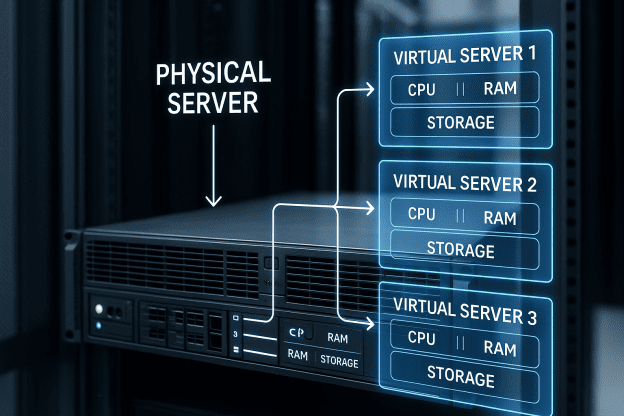
So, if you’re asking, “What is virtualization?”—virtualization is a software-based infrastructure technology that serves as an alternative to conventional operating systems. It enables the installation and management of multiple operating systems on the same system or server hardware.
Based on the diagram above, each operating system corresponds to a virtual server, known as a Virtual Private Server (VPS). With this definition, you now have a clear idea of what a virtual server actually is.
What is a Virtual Private Server (VPS)?
The internet is an immense network connecting computers located across the globe. When two computers are connected and exchange data, they form a small network. On the internet, all the world’s computers are connected via cables, each with a unique address for identification and access. When you’re connected to the internet, it means your system is part of this massive network, serving or receiving services with a unique address on the internet.
In this massive network, some systems act as servers. For instance, when you open a website in a browser, the content is hosted on a system within the internet network that has web server software installed, holding the site’s data. Such websites can contain a lot of data or may be accessed by numerous users worldwide simultaneously, making it impossible for these websites to be hosted on a simple computer system.
When the hardware resources of a physical server are divided into independent, virtual sections using virtualization software, virtual servers with standalone and limited resources are created. These servers are known as Virtual Private Servers (VPS). This type of service offers features similar to a dedicated server, but with limited capabilities and lower costs compared to a dedicated server.
.
Defining VPS at a Glance
| 1 | Common Terms | Virtual Server, VPS, Virtual Private Server. |
| 2 | Access and Connection Methods | VNC / Remote Desktop / Putty |
| 3 | IP Type | Static and dedicated IPs |
| 4 | DNS Type | Dedicated DNS |
| 5 | Control Panel Options | DirectAdmin, cPanel |
| 6 | Operating Systems | Windows, Linux |
| 7 | Geographical Locations | America and Europe available |
.
.
What Does a Data Center Mean?
To answer the question, “What is a data center?” We need to first understand that servers have powerful hardware and network requirements and generate significant heat, making their power consumption very high. Due to these conditions, servers cannot be stored in regular spaces like homes. The location where servers are stored needs to have an industrial-strength power system, appropriate cooling systems, and high-bandwidth internet connectivity.

A Data Center is a facility designed to meet these needs, providing a secure and suitable environment for servers. Data centers are standard facilities that are highly resistant to natural disasters, feature robust internet infrastructure with extremely high bandwidth, and are equipped with advanced power systems, including multiple sources to ensure uninterrupted electricity. They also use specialized, advanced cooling and ventilation systems.
While these technical details explain what a data center is, as a user, you won’t need to worry about most of these aspects when purchasing or using a VPS. What you should pay attention to are the geographical location of the data center and its network quality.
Understanding Traffic in VPS
Traffic refers to the total volume of data consumed for downloading and uploading. Put simply, every time a user views a page from your website, downloads a file, or performs some activity on your system, data is transferred either from the server to the user or vice versa. This process generates traffic. Server traffic is a key factor in a website’s performance because excessive traffic can lead to slow website speeds or even total loss of access. Managing server traffic is especially crucial for high-traffic websites to ensure high-quality services and fast page loads.
What is Bandwidth in VPS?
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred between the server and users in a specified time frame. Essentially, bandwidth is the limit that determines the amount of traffic the server can handle. This includes loading web pages, downloading files, sending data, and processing user requests. Higher bandwidth means the server can handle more traffic without experiencing slowdowns or disruptions.
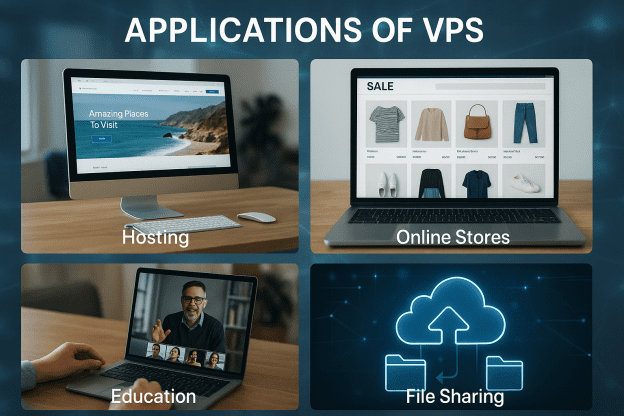
Applications of VPS
The applications of Virtual Private Servers are vast and versatile. Below are examples and general categories of tasks that VPS can be utilized for.
.
- Website Hosting
If your website has a lot of traffic, and regular hosting cannot meet your demands, upgrading to a VPS or dedicated server can help manage higher traffic levels efficiently.
- Online Stores
Online stores, especially those with a large inventory and customer base with high transactional activity, require reliable hosting solutions. VPS is ideal for such platforms to ensure fast, smooth shopping experiences.
- Virtual Education Platforms
Hosting virtual classrooms is not optimal with shared hosting. If your virtual classroom has fewer than 100 simultaneous participants, a VPS is recommended. However, for larger classes, a dedicated server would be a better choice.
- File and Video Sharing Sites
Websites that facilitate sharing large files or videos—whether publicly or privately—would benefit greatly from the storage space and performance advantages of a VPS.
- Custom-Coded Websites
Some websites rely on specialized programming technologies, requiring extensive access to the hosting server. Regular hosting doesn’t allow such customization, making VPS a preferred option. For instance, websites that use custom PHP frameworks like Laravel or ASP frameworks benefit greatly from a VPS.
- Shared Services
In some companies or organizations, shared services and software are required across branches that are geographically distant. In such cases, VPS provides the ideal solution to ensure reliable connectivity between all points.
- Email Services
Many businesses and organizations use personalized email services hosted on private servers. A VPS can be used to host these services, ensuring secure and efficient email management.
- Databases
Applications using databases with large volumes of data can store these on a separate VPS for enhanced security and storage capabilities.
- Application Servers
Certain companies and organizations use specialized application software that needs to be accessed by branches at different locations. Examples include accounting software that can be hosted and accessed securely with a VPS.
- Software Development and Production
Nowadays, many software developers require specific resources for software development projects. If these projects are significant, it becomes necessary to set up VPS servers for developers needs.’
- Git Service
The Git service is used for online versioning and backup of programs under development. Multiple developers from various locations can upload their code onto a VPS.
- Project and Code Management Services
If you have separate software development teams or developers working remotely or on a project-by-project basis, you can use VPS to manage your projects and codes securely and collaboratively.
- Monitoring and Management Operations
If you’re running a factory, office, workshop, or any location you wish to monitor or manage remotely online, a Virtual Private Server might be required.
- Surveillance Cameras
VPS can be employed to run surveillance cameras, allowing users to remotely monitor locations live via the internet.
- Management Systems and Software
For centralized management systems, such as task management systems, VPS is one of the best solutions to ensure accessibility, performance, and organization.
.
Advantages and Disadvantages of VPS
Like any tool, VPS has its pros and cons. Understanding these advantages and limitations can help you make better use of your VPS or choose the most suitable option for your specific needs.
Advantages of VPS
Some benefits of using VPS include the following:
- Cost-effective: VPS is far less expensive compared to dedicated servers.
- Root Access: Allows full administrative control and configuration.
- Ease of resource allocation: You can easily adjust server resources.
- Better security and speed: Compared to shared hosting, VPS provides higher security and faster performance.
Disadvantages of VPS
Although VPS has fewer disadvantages than other types of hosting, here are some cons to consider:
- Higher cost compared to shared hosting.
- Server configuration is usually difficult—users may need coding skills or technical knowledge for server management.
- Offers fewer resources than dedicated servers.
Types of VPS
When buying a virtual private server, you’ll come across various types. Below, we will classify VPS based on several criteria.
Types of VPS Based on Operating System
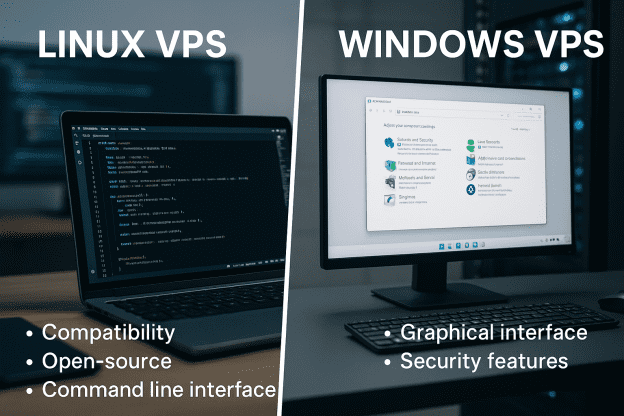
One of the primary criteria for choosing a VPS is its operating system. Generally, servers can be installed with two main operating systems: Linux and Windows. Let’s delve into these types based on operating systems.
- Linux VPS
Linux is one of the most commonly installed operating systems on servers. It offers high flexibility and security to users and is widely favored for these attributes. One of its other advantages is that Linux is an open-source system, so it is entirely free to use.
Features and Applications:
- Compatibility: Ideal for websites built using programming languages like PHP or related frameworks (e.g., WordPress or Laravel).
- Various Distributions: Linux offers various distributions, such as Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian, allowing you to choose one based on your project’s needs.
- Open-Source Nature: Free installation of a variety of software and tools.
- Web Servers: Easily works with web servers like Apache, Nginx, and LiteSpeed.
It is important to note that Linux differs slightly from Windows, particularly in server management. If you’re a Windows user transitioning to a Linux VPS, you’ll likely encounter new challenges, particularly regarding management methods. To simplify Linux server management, graphical control panels such as cPanel or DirectAdmin are available.
- Windows VPS
Windows VPS utilizes Microsoft’s server-specific operating systems that are optimized for server management tasks.
Features and Applications:
- GUI: Offers a graphical interface similar to Windows desktop, simplifying usability, especially for beginners.
- Microsoft Compatibility: Works well with Microsoft software like SQL Server.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): Allows remote server management efficiently.
Features and Applications of Windows VPS
- Graphical Interface (GUI): Unlike Linux, which is primarily managed through a command-line interface, Windows VPS offers a graphical environment similar to Windows desktop, making it user-friendly even for beginners.
- Compatibility with Microsoft Software: This type of VPS is particularly suitable for running official Microsoft products and services such as SQL Server.
- Ease of Management: Thanks to its graphical interface, even less experienced users can effectively manage Windows VPS.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): Access and manage the VPS remotely via the RDP protocol, enabling convenient and secure management.
Read More: VPS vs RDP
.
.The Drawbacks of Windows VPS
If your data center is located outside your home country, licensing compliance (such as abiding by Microsoft’s copyright laws) may require purchasing an official Windows Server license, potentially making Windows VPS more expensive than Linux VPS. However, if you plan to use official Microsoft applications, Windows VPS is an ideal option.
.
Linux Distributions for VPS
Linux-based VPS comes in many different distributions. These distributions share the same basic Linux kernel but are tailored to suit various requirements. Some of the popular distributions that can be installed on VPS include:
- Ubuntu: Popular for its simplicity and widespread community support.
- CentOS: Favored for its stability and frequent use in enterprise hosting environments.
- Debian: Known for its security and efficient package management.
- Fedora: For cutting-edge technologies and shorter release cycles.
Keep in mind that Linux distributions are not limited to these; however, the above-mentioned distributions are the most common for use in server environments.
MikroTik VPS
MikroTik is essentially a router operating system and is known for its lightweight nature. If you were to summarize the key advantage of MikroTik VPS in one sentence, it would be its capability to control server bandwidth consumption. Moreover, this server allows you to restrict specific IP addresses that may pose a security threat, thus enhancing overall server security.
Features and Applications of MikroTik VPS:
- RouterOS Operating System: A specialized OS capable of being installed on both servers and desktop computers.
- Advanced Routing: Primarily used for network settings, routing, and managing traffic in extensive networks.
- High Stability: An excellent choice for businesses requiring advanced network control and management.
Types of VPS Based on Control Panels
VPS servers can run on almost any virtual operating system. However, servers typically host server-optimized operating systems for efficiency and resource maximization.
VPS management and security are entirely the responsibility of the user. Hosting companies typically don’t guarantee their maintenance beyond initial server provision. Therefore, managing VPS servers requires expertise and time, and in some cases, even a skilled professional.
To simplify the management of VPS, web-based control panel software has been developed. These control panels simplify server administration by providing a graphical
Popular control panels for VPS management are:
DirectAdmin
- A web-based control panel designed for Linux-based hosting environments.
- Affordable: Offers the most economical license pricing compared to its competitors.
- Modular: Additional security and management modules can be installed as needed.
- Intuitive: Provides a user-friendly interface.
- Regularly Updated: Continuously improved through updates.
- Servers that use DirectAdmin for management are known as DirectAdmin VPS.
cPanel
- One of the most popular control panels for Linux-based hosting.
- Known for its highly user-friendly interface.
- Strong default security: Additional modules can be added for enhanced protection.
- Excellent modularity and regular updates.
See: cPanel VPS
Plesk
- The most popular control panel for Windows-based hosting.
- Extremely intuitive and user-friendly interface.
- Good default security settings, with options for improved customization.
- Servers using this control panel are referred to as Plesk VPS.
Webmin
- A Linux-based web management panel and one of the most popular free options.
- Enables complete server management.
- Simple installation process.
- Downsides: Updates are sometimes delayed, and default security measures are lacking.
- It is modular and can be used to install and manage various system services through a user-friendly interface.
Virtualmin
- A sibling product of Webmin designed for Linux server hosting management.
- Also a free tool, specifically designed for managing web hosting environments.
- Regularly updated and has moderate default security.
- Modular and efficient, with high usability for minimal effort.
.
.
VPS Based on Management Levels
Virtual private servers can also be categorized based on the level of management provided by the hosting provider. Generally, these levels include:
1. Unmanaged VPS (Self-Managed VPS)
This is the cheapest type of VPS, offering minimal support from the hosting provider. In this case, the hosting company provides the required hardware and resources, but the rest of the responsibility is up to you.
Your Responsibilities with an Unmanaged VPS:
- Maintaining and managing the server.
- Installing and configuring software.
- Applying updates.
- Securing the server and data.
Who Should Use Unmanaged VPS?
Unmanaged VPS is suitable for advanced users, developers, and IT professionals who have the necessary technical expertise to handle server administration. An unmanaged VPS provides complete root access, allowing for high levels of customization.
.
Semi-Managed VPS
A semi-managed VPS provides a combination of automated management by the hosting provider and user responsibilities.
Provider Responsibilities:
- Managing hardware and underlying infrastructure.
- Performing essential updates to the operating system.
- Addressing server-related technical issues and offering limited support.
User Responsibilities:
- Managing the website’s content, design, and marketing.
- Installing plugins and custom software as needed.
- Ensuring the security and performance of applications.
Who Should Use a Semi-Managed VPS?
This option is best suited for users with basic technical skills but who need occasional support with complex technical tasks.
3. Fully Managed VPS
A fully managed VPS offers complete management by the hosting provider, allowing users to focus entirely on running their business or website without worrying about technical issues.
Provider Responsibilities:
- Full server management, including installation, updates, and maintenance.
- Fixing hardware and software problems.
- Providing complete security, such as firewalls, patches, and constant monitoring.
- Conducting daily backups.
- Offering full customer support.
Who Should Use Fully Managed VPS?
Fully managed VPS solutions are ideal for users who lack technical knowledge or prefer not to spend time on server management.
Types of VPS Based on Usage
So far, most of the content we’ve covered has focused on VPS hosting for websites. However, virtual private servers have many other use cases. If you’re wondering what other applications a VPS might have, here are some of the most significant:
Trading VPS
These days, working in the cryptocurrency market is one of the most popular activities for individuals worldwide. Many people spend their time analyzing cryptocurrency charts and candlestick patterns to buy and sell for profit.
One effective solution for bypassing these restrictions is using a trading VPS. A trading VPS allows you to connect to these exchanges using a fixed IP address from another country (e.g., Germany) and conduct trading activities without restrictions.
Forex VPS
The Forex market, another major branch of financial trading, deals with the exchange of currencies. For instance, a trader may exchange Canadian dollars for Chinese yuan, a process referred to as “currency pair trading.”
VPS for Hosting
A hosting VPS is a virtual server specifically optimized to host websites. Using such a server improves the performance of websites significantly. For example, the most noticeable impact is the enhanced page loading speed. Apart from creating a better user experience and increasing customer satisfaction, this performance boost positively influences your website’s SEO rankings.
However, it’s essential to keep in mind that hosting VPSs are exclusively configured for hosting websites. In other words, this type of server is not suitable for other types of activities.
Warez VPS
A Warez VPS is a type of virtual private server that allows you to upload and host cracked or pirated software and use such software without restrictions.
It’s worth mentioning that in countries where copyright laws are strictly enforced, uploading pirated files or using cracked software on VPS servers is prohibited. If you require such functionality, a Warez VPS is an appropriate choice for your needs.
SSD VPS
Technological advancements in hardware play a crucial role in the performance of VPS servers. One such advancement is the adoption of Solid State Drives (SSD) in server storage.
Since SSD drives provide significantly higher speeds compared to traditional HDD drives, utilizing SSD storage in a server greatly enhances data transfer rates and overall server performance. Servers equipped with SSD technology are referred to as SSD VPS.
VPS for Online Conferences
The evolution of internet technology has enabled people to connect remotely for professional meetings or virtual conferences. For example, many seminars and discussions are now conducted online with ease.
However, if you intend to host a large virtual conference with numerous speakers and participants, you’ll require a powerful server capable of providing seamless audio-visual communication without interruptions. A conference VPS is designed for this very purpose, making it an ideal option for organizing virtual events efficiently and securely.
Low-Ping VPS for Gaming
The last type of VPS we’ll mention here is one specifically optimized to lower ping times, which is crucial for gamers. For gamers seeking to play online multiplayer games without lag, using a low-ping VPS ensures reduced delays and smooth gameplay.
Applications of VPS in Crypto and the Stock Market
Virtual private servers are essential in the cryptocurrency and stock market trading ecosystem. Trading VPS solutions allow traders to operate efficiently without disruptions caused by local internet issues, power outages, or other technical obstacles.
Using a Forex VPS, for instance, helps reduce latency and slippage, enabling traders to execute trades quickly in near real-time. This capability allows traders to take advantage of market opportunities while reducing the risks of technical failures.
In addition, while VPS isn’t suitable for direct cryptocurrency mining due to hardware resource limitations, it can be used to remotely manage mining operations or monitor cryptocurrency-related projects.
VPS for Telegram Bots
A VPS can also be used to host Telegram bots, enabling them to operate 24/7 without interruptions. With a VPS, Telegram bots remain consistently online and respond to user requests with minimal delays. This setup significantly improves the stability, security, and responsiveness of the bots, especially those requiring constant availability and high processing performance.
VPS in Gaming
In online gaming, VPS servers are utilized to host game servers, manage multiplayer platforms, and enhance the gaming experience. These servers offer low ping, stable connections, and optimized performance, ensuring smooth gameplay without delays. Additionally, developers can leverage VPS to create custom private servers for their gaming communities.
Read More: VPS Use Cases
Free VPS: Is It Worth It?
A free VPS is a basic version of a virtual private server provided for users to test services, learn hosting basics, or carry out small-scale projects without cost. However, it comes with many limitations, including lower bandwidth, limited storage, and weaker performance.
For users looking for long-term hosting solutions with better reliability and enhanced resources, purchasing affordable VPS hosting is highly recommended as it offers better capabilities and cost efficiency compared to free alternatives.
What is an Hourly VPS?
An hourly VPS is a type of virtual private server where you pay only for the time you actually use the service. This option provides great flexibility, as it’s particularly suited for short-term projects, testing software, or running temporary tasks.
What is the Most Important Criterion for Choosing a VPS?
When selecting a virtual private server, it’s essential to assess your requirements carefully and then compare the available options. Here are some critical factors to consider:
- RAM Size: The amount of RAM directly affects your VPS performance. Choose according to your hosting and resource needs.
- Storage Type and Size: Decide whether an HDD or SSD server suits your needs based on your workload and the volume of data you plan to store.
- Processor (CPU): Select a server with sufficient processing power to handle complex tasks or high-traffic sites.
- Management Level: Depending on your technical skills, choose between managed, semi-managed, or unmanaged VPS services.
- Operating System (Linux vs. Windows): Consider the compatibility of the operating system with the applications you plan to run.
- Server Location: If your target audience is in a specific country, opt for a VPS located geographically close to them for reduced latency and better speeds.
- Reliability (Uptime): Choose a provider that guarantees at least 99.5% uptime in their Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- Hardware and Upgradability: Confirm whether the VPS hardware is modern and supports resource upgrades as your needs grow.
- 24/7 Support: Ensure that your hosting provider offers round-the-clock technical support through email, chat, or phone to address urgent issues.
- Provider Reputation: Select a VPS provider with a reliable track record of performance, support, and security.
Which Data Center Should You Choose for Your VPS?
When selecting a data center, keep the following points in mind:
1. Network Security of the Data Center
Some data centers, such as OVH, offer excellent built-in network security. Make sure your chosen data center has strong defenses against threats like DDoS attacks.
2. Geographic Location of the Data Center
The location of the data center depends on your needs. It’s generally recommended to choose a server located in the region where most of your website’s traffic originates. For instance, if your visitors are from the USA, an US-based VPS might be the right choice, while European servers may be suitable for European audiences.
3. Support for Warez Traffic
If you require hosting services for non-standard traffic (such as cracked software or security penetration tests, known as Warez traffic), confirm that the data center permits and supports this type of activity. Keep in mind that most major data centers located in countries with strong copyright enforcement policies do not allow warez traffic.
Virtualization Platforms and Technologies
The infrastructure for virtualized servers can vary based on the technology used by the hosting provider. The most commonly used virtualization technologies include KVM and VMware, with others like XEN having their own niche use cases.
1. XEN
XEN is not free and is considered one of the more advanced virtualization platforms. It is primarily used in large organizations or specialized corporate environments rather than by most hosting companies. This is due to its complexity and high licensing costs, which make it less practical for providing affordable VPS services.
2. VMware
VMware is the most well-known and popular virtualization platform worldwide. Most major hosting companies, businesses, and organizations use VMware.
The primary product for virtualization offered by VMware is ESXi, which is a lightweight and highly efficient operating system designed specifically for creating virtualized environments.
ESXi Features:
- Extremely stable platform.
- Powerful hardware management capabilities.
- Advanced fault-tolerance mechanisms for maintaining uninterrupted server performance.
Many hosting providers also integrate ESXi with custom management panels, allowing users to easily manage VPS servers, reboot systems, or monitor performance.
3. KVM
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a widely used, open-source virtualization technology based on Linux. While KVM itself is free, hosting providers often use premium management panels with it to provide users with intuitive interfaces for managing servers.
Key Features of KVM:
- Custom Operating System Installs: Users can install or reinstall operating systems, such as Linux or Windows, at their convenience.
- Highly Flexible Management Tools: KVM provides better user experience with tools like SolusVM or AutoVM, which simplify server management.
- Faster Delivery and Deployment: Virtual servers built on KVM can be provisioned and delivered quickly, making it an excellent choice for immediate or time-sensitive needs.
Note: KVM is highly popular among VPS users because it offers a seamless combination of affordability, flexibility, and performance.
Hard Drive Management in VPS
Storage capacity is an ongoing issue across all computer systems, including VPS hosting. If the storage capacity of a server’s hard drive becomes fully consumed, it can severely disrupt server operations. One common misunderstanding among users is believing that hard drive space on VPS servers is shared among users. Let’s clarify:
- In VPS servers, the hard drive space is entirely dedicated to the user. No matter the virtualization technology (KVM, VMware, etc.), each user receives their own allocated storage.
Overselling: The Risk
While VPS storage is technically dedicated to each user, some hosting providers oversell their servers, meaning they assign more storage capacity across accounts than the physical server can handle. This practice can lead to significant performance degradation for all users on that server.
Tip: To avoid potential issues caused by overselling, make sure you choose a trusted hosting provider with a solid reputation.
What is VNC Access or Console Access?
Users access their VPS via the internet. However, if there’s a problem with your internet connection or you need to perform operations that occur before the operating system is fully booted, you won’t be able to connect remotely using traditional methods like RDP or SSH. This is where console access (VNC) becomes useful.
VNC (Virtual Network Computing) simulates direct physical access to your VPS, as though you’re sitting in front of the physical server with a keyboard, mouse, and monitor. Console access allows users to fix boot-level issues or conduct system reconfigurations, regardless of the server’s operating system status.
How to Increase VPS Security
Security is a critical consideration when using VPS. Many VPS-related security responsibilities fall on the user, requiring adequate knowledge and proper precautions to secure the system. Hosting providers generally secure the hardware and network infrastructure, but the rest lies in your hands.
.
.
.
.Here are some simple steps you can take to secure your VPS:
- Change Default Login Credentials: Always change the initial username and password provided by your hosting provider upon delivery of the VPS.
- Use Strong Passwords: Avoid predictable passwords and update them regularly, as VPS servers are often the target of brute-force attacks.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Shut down unused services to reduce the attack surface of your VPS.
- Enable a Firewall: Use a firewall to control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Restrict Open Ports: Close all unused ports and keep only the necessary ports open (e.g., change SSH’s default port 22 to another value).
- Restrict IP Access: If specific users or locations access the VPS (e.g., a company office), limit access to designated IP addresses only.
- Install Security Tools: Consider using tools and modules to prevent brute-force attacks and enhance overall server protection.
- Backup Your Data Regularly: Regularly create backups of your data. If you’re unsure how to do this, coordinate with your hosting provider. Note that some providers may charge extra for backup services.
Comparison: VPS vs. Dedicated Servers vs. Shared Hosting
Each type of server—Shared Hosting, Virtual Private Server (VPS), and Dedicated Server—offers unique features and benefits. Choosing between these options depends on your specific requirements and budget. Below is a detailed comparison:
1. Shared Hosting
In shared hosting, multiple websites are hosted on a single server, sharing resources like RAM, CPU, and storage. It is an affordable solution for small websites with minimal traffic.
Advantages of Shared Hosting:
- Low cost.
- Simple to set up and manage, even for beginners.
- Minimal technical knowledge required.
Disadvantages of Shared Hosting:
- Limited resources.
- Poor performance during traffic surges.
- Security risks due to shared infrastructure.
2. Virtual Private Server (VPS)
VPS provides dedicated resources to users by creating multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. It is the middle ground between shared hosting and dedicated servers.
Advantages of VPS:
- Dedicated resources with enhanced reliability.
- Greater control and customization.
- Superior performance compared to shared hosting.
Disadvantages of VPS:
- Higher cost than shared hosting.
- Requires some technical expertise to manage.
- Resources are still shared with other VPS users on the same host machine.
3. Dedicated Servers
In a dedicated server, all resources (CPU, RAM, storage) are allocated to a single user. This option offers the highest level of performance, flexibility, and security.
Advantages of Dedicated Servers:
- Full resource allocation.
- High levels of customization.
- Exceptional performance and reliability.
- Superior security.
Disadvantages of Dedicated Servers:
- Expensive compared to VPS or shared hosting.
- Requires significant technical knowledge or a dedicated IT team for management.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS | Dedicated Server |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High |
| Performance | Limited | Moderate | Excellent |
| Security | Low | Moderate | High |
| Resources | Shared | Partially Dedicated | Fully Dedicated |
| Target Audience | Small websites/new users | Growing businesses | Large organizations |
| Customization | Low | High | Full |
Conclusion: VPS offers the perfect balance between affordability and performance for growing websites, whereas dedicated servers are better suited for enterprise-level applications.
Major Differences Between VPS and Cloud Servers
Both VPS (Virtual Private Server) and Cloud Servers are popular hosting options. While they have similar uses, their underlying infrastructures and capabilities vary greatly. Below is a breakdown of their key differences:
1. Performance
VPS:
VPS provides a consistent and stable level of performance because resources (RAM, CPU, and storage) are dedicated to each user. However, since these resources are limited to a single physical server, the performance may degrade if the server experiences heavy loads.
Cloud Server:
Cloud servers, on the other hand, utilize a network of interconnected servers. If the workload increases, the server can easily tap into additional resources from other servers within the network. This ensures stable performance, even under high-pressure situations.
2. Scalability
VPS:
Scaling VPS resources is relatively limited. For example, increasing RAM, CPU, or storage often requires migrating to a completely new VPS.
Cloud Server:
Cloud hosting is highly scalable. Users can adjust resources (e.g., increase CPU cores, storage, or bandwidth) almost instantly without interruptions, simply by submitting a request or making changes through the hosting provider’s dashboard.
3. Security
VPS:
VPS security depends on how well the user configures their server. Users need to implement appropriate measures (e.g., firewalls, updates, backups) to protect their VPS. If security measures are neglected, vulnerabilities may arise.
Cloud Server:
Cloud servers are inherently more secure because hosting providers manage most security aspects, such as data backups, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) protection, and server redundancy. Additionally, data is typically spread across multiple servers, enhancing protection against server failure or data loss.
4. Customization
VPS:
With VPS hosting, users have root-level access and can fully customize their virtual server, including choosing their preferred operating system, software configurations, and server settings.
Cloud Server:
Cloud hosting, although flexible, often comes with pre-set configurations from the provider, limiting users’ control over certain advanced settings. For higher levels of customization, users may need to purchase premium packages.
5. Redundancy (Backups and Failover Systems)
VPS:
VPS generally lacks built-in redundancy. All your data resides on a single server, which means if the physical server crashes, your data could be compromised unless you’ve taken regular backups.
Cloud Server:
Cloud servers utilize a redundancy model, where data is stored and backed up across multiple servers. Even if one server fails, another server in the cloud network immediately takes over, ensuring continuous service without interruptions.
6. Cost
VPS:
VPS hosting is often more affordable because it’s based on shared physical server resources. The pricing is typically fixed and predictable, making it ideal for those with tight budgets.
Cloud Server:
Cloud hosting is more expensive than VPS due to its flexibility, scalability, and redundancy. However, with pay-as-you-go pricing models, users only pay for the resources they use, which can help manage costs for some scenarios.
.
.
.
Summary of Differences Between VPS and Cloud Servers
|
Feature |
VPS |
Cloud Server |
|
Performance |
Stable, but limited to physical server capacity. |
Highly stable and resource-flexible. |
|
Scalability |
Moderate—requires migrations. |
High—resources scale instantly. |
|
Security |
Depends on user’s configurations. |
Provider-managed with built-in security. |
|
Customization |
High—complete root access. |
Moderate—preset configurations. |
|
Redundancy |
Low—no redundancy on a single server. |
High—data distributed across servers. |
|
Cost |
Affordable with fixed pricing. |
More expensive; pay-as-you-go pricing. |
.
.
What Role Does a Virtual Machine Play in VPS?
Virtualization is the backbone of the VPS concept. Virtual servers rely on virtual machines (VMs), which are separate environments created on top of a single physical server. Virtualization splits the server’s resources (such as CPU, memory, and storage) and assigns them to individual virtual servers.
Each virtual machine functions as though it were an independent physical server. It has its own operating system, applications, and data. This structure is managed by software called a hypervisor, which is responsible for resource allocation, managing virtual machines, and ensuring stable performance.
.
The Difference Between VPN and VPS
It’s common to confuse VPN and VPS because of their similar-sounding names. However, these two technologies serve entirely different purposes:
What is a VPS?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a server created by dividing a physical server into several virtual servers using virtualization technology. It is primarily used for hosting websites, running applications, or managing data.
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a security-focused technology that encrypts internet traffic and creates a secure connection to protect online privacy. It’s often used to bypass geographical restrictions or access censored content.
Read More: VPS vs VPN
.
Key Differences Between VPS and VPN
|
Aspect |
VPS |
VPN |
|
Purpose |
Hosting websites, apps, databases. |
Ensuring online privacy, bypassing restrictions. |
|
Users |
Developers, businesses, IT teams. |
General users, security-focused professionals. |
|
Benefits |
Dedicated resources, scalability. |
Encryption, IP masking, anonymity. |
|
Management |
Requires technical setup and expertise. |
Simple—usually works with installed software. |
.
.
.
Buy a VPS with Mixal
.
Virtual Private Servers (VPS) offer flexibility, scalability, and affordability, making them a top choice for hosting websites, running applications, and more. With Mixal, you not only get high-performance VPS solutions but also expert guidance to buy
and set up your VPS from scratch.
.
Our team at Mixal ensures a seamless experience, from easy setup instructions to 24/7 support, helping your business grow with a scalable VPS solution. Start with Mixal today
and get the resources you need for success.
.
.
Virtual Private Servers offer flexibility, scalability, and affordability, making them a preferred option for many. Below are some frequently asked questions to consider before buying a VPS.
.
.
.
Frequently Asked Questions
.
●Yes, in most VPS setups, the network and bandwidth are shared among multiple users. If you require dedicated bandwidth, you’ll need to discuss this with your provider.
.
●Yes, storage in a VPS is allocated exclusively to you. However, the management and allocation methods may vary depending on the virtualization technology.
.
●The most important factors include RAM, storage (HDD/SSD), and the geographical location of the server.
.
●A VPS offers dedicated RAM, CPU, and storage. These resources are exclusive to your server and cannot be accessed by other users.
.
●Network bandwidth and physical server space (CPU hardware) are shared with other VPS users on the host system.
.
●The virtualization platform doesn’t usually matter to end users, as it remains hidden from their view. However, users who are familiar with certain platforms may prefer options like VMware or KVM based on past experience.
.
●The hosting provider is responsible for installing, setting up, and delivering the VPS. Users typically receive login credentials (like SSH or RDP) after setup is complete.
.
●A managed VPS includes a pre-installed control panel, making it easier to manage and configure server operations through a graphical interface.
.
●Upgrade your VPS when your website or application needs more resources (e.g., RAM, CPU, storage) or when the current server struggles with increased traffic.
.
.

